One of many world’s least-exciting sentences is, “Let’s speak about expertise requirements!” However I promise I’m not digging down into wiring schematics, pinout diagrams, and 1,000-page protocol descriptions. Relatively, I wish to enable you stand up to hurry on how USB and Thunderbolt work individually and collectively so you understand how one can finest use them—and troubleshoot them when incompatibilities come up.
The trail ahead depends on the most recent requirements: Thunderbolt 4 and USB4. Whereas not completely suitable with one another, they’re practically so. Most significantly, the 2 requirements have successfully converged on a single cable kind you should buy and use virtually universally with Thunderbolt 3 or 4, and USB 3.1, 3.2, and USB4 by way of USB-C.
The next is an edited excerpt from Glenn Fleishman’s ebook, “Take Management of Untangling Connections,” a information to USB, Thunderbolt, DisplayPort, HDMI, Ethernet, and video connections and troubleshooting, out there from Take Management Books.
USB: the as soon as and future common commonplace
USB was at one level the good hope of the long run: Common! Serial! Bus! All three phrases pointed in the correct course. As a substitute of many serial connectors and buses (and even some parallel ports), USB would unify many sorts of function into one controller with a restricted set of jacks and plugs designed for various functions. All USB gadgets might plug into any USB port, given the correct cable.
A beautiful concept, however one which was ruined by the big variety of USB plug sorts that emerged. There are presently 9 sorts of USB connectors. However that’s not the one challenge: despite the fact that it’s possible you’ll be most acquainted with the oblong USB Kind-A plug and jack, a USB cable can’t have a Kind-A plug on each ends, whether or not full-sized, Mini, or Micro.
In a chart from Wikipedia’s intensive USB entry, proven beneath, the eight sorts of USB connectors run throughout the highest and down the facet. The next factors are value noting:
- Kind-A can’t connect with Kind-A: it’s famous as “Proprietary, hazardous” (the pale purple squares) because it’s that harmful and dangerous.
- The profusion of purple squares studying “No” additionally assist inform the story in regards to the lack of like-to-like and even unlike-to-unlike choices.
- Throughout the highest, you possibly can see Kind-A was as soon as probably the most suitable, connecting to all of the B sorts (4 of them) after which to USB-C.
Nevertheless, the ultimate column reveals the reality and the evolution: USB-C can connect with most codecs—principally importantly, to itself. (Mini-A and Micro-A are so uncommon, it’s not an actual lacking hyperlink that USB-C can’t work with them.) I’ll return to USB-C in a second.
USB’s requirements evolution

USB-IF
As USB connector sorts proliferated, the underlying technical commonplace advanced, too. The evolution drove the newer connection codecs. USB from 1.0 to three.0, and from 1.5 Mbps/12 Mbps to five Gbps, typically relied on the identical rectangular Kind-A connector. USB 1.1 (1998) grew to become broadly used and was significantly helpful for keyboards, mice, and different enter gadgets. USB 2.0 (2000) provided 480 Mbps, offering a fee appropriate for exterior exhausting drives, and contending for just a few years with FireWire 400 and 800 (Apple’s selection). However USB gained out.
Its requirements affiliation, the USB Implementers Discussion board (USB-IF) launched USB 3.0 in 2008, skyrocketed the information fee to five Gbps. Marketed as SuperSpeed, it additionally bumped up energy circulate from 150 milliamps (mA) to 900 mA, permitting for cellular machine charging and bus-powered peripherals.
It was solely 2014 that the USB-C connector debuted with USB 3.1. Kind-A connectors had been restricted to five Gbps, however USB 3.1 Gen 2, because it was referred to as, might attain 10 Gbps with computer systems and peripherals outfitted with applicable {hardware}. In 2017, that was bumped upward once more with USB 3.2. A 3.2 Kind-A connector can provide 5 or 10 Gbps; a USB-C connector, 10 or 20 Gbps. The USB-IF rebranded its requirements names, too, to SuperSpeed USB 5 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 20 Gbps.

USB-IF
That is the place I ask you to carry on to your socks and take away the area between USB and a digit. USB4 (see, no area) solely permits for USB-C connectors and is an implementation of…Thunderbolt 3! USB4 can function at both 20 Gbps or 40 Gbps; within the latter type, it’s marketed and labeled as SuperSpeed USB 40 Gbps.
The evolution of USB was subsequently away from profusion and towards the USB-C single jack/plug kind that would work in every single place—really common eventually!
The Emergence of USB-C
Lastly, a single connection kind that was used on each ends of a cable, reversible by 180° as a plug inserted right into a jack throughout its lengthy finish, had a compact issue, and will carry as much as 100 W of energy (and, later, as much as 240 W). Energy circulate might go both approach: a laptop computer or desktop might cost a cellular machine or energy pack, or vice versa.
With Intel’s adoption of USB-C beginning with Thunderbolt 3 and the near-complete convergence of USB on Thunderbolt requirements, it’s all excellent, isn’t it?
Nicely, no. First, individuals had invested loads into tools that had USB Kind-A connectors. Early computer systems with USB-C jacks tended to scrimp, and docks with many USB Kind-A ports had been briefly provide. From 2015 to a minimum of 2019, individuals complained endlessly—and largely rightly so—that they’d to purchase and preserve useful a big array of cables, adapters, and mini-docks. By 2020, it appeared to calm down: peripherals switched to both be USB-C based mostly or included a cable or adapter, less-expensive docks had been broadly out there, and pc makers—significantly Apple—determined to incorporate extra and completely different sorts of jacks to scale back the trouble.
Second, in the course of the awkward Thunderbolt 3, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, Thunderbolt 4, and USB4 transition, you can wind up shopping for a USB-C cable that wouldn’t correctly join two gadgets with USB-C ports, wouldn’t join them on the highest potential information fee (dropping to 10 Gbps, say, as a substitute of 40 Gbps), or would solely go 15 W or 60 W of energy as a substitute of 100 W. That drawback nonetheless hasn’t gone away, but it surely has decreased and can enhance much more within the close to future.
Third, as USB has moved from 3.1 to three.2 to 4, and added choices for energy provided by ports and carried by cables, the profusion of markings has grow to be greater than baroque.
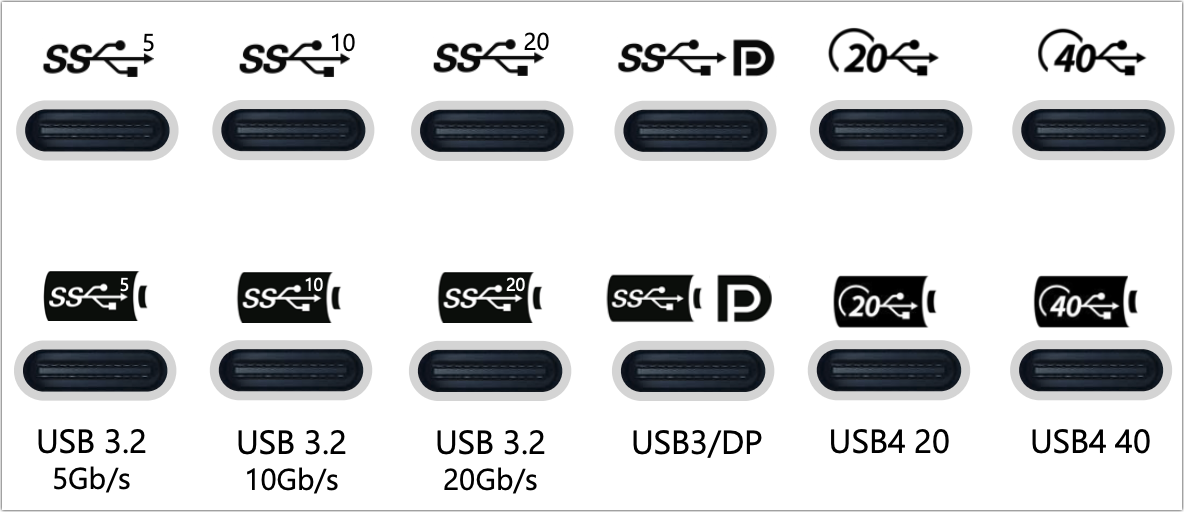
Intel
Thunderbolt doesn’t change USB, however the convergence of it with USB does assist clear away among the underbrush, as I clarify subsequent.
The Thunderbolt commonplace
Intel launched Thunderbolt underneath the title Gentle Pace in 2010 and Apple—then a eager person of Intel CPUs—helped set the course adopted it in all their computer systems. The unique model of Thunderbolt provided what was then a blazing 10 Gbps of knowledge concurrently in each instructions—so blazing that it outstripped most storage and different {hardware} of the time.
Recognizing the scarcity of ports on computer systems on the time, Thunderbolt was constructed from the beginning with help for daisy chaining, related in idea to the sooner SCSI commonplace, and one thing that made sense for stringing collectively a collection of high-performance optical drives, exhausting drives, or arrays of drives in a single enclosure (RAID). As much as six Thunderbolt gadgets could possibly be daisy chained.
The unique Thunderbolt additionally allowed DisplayPort to go over the identical connection, and will present a minimum of 10 W of energy.
Intel doubled throughput to twenty Gbps in 2013 with Thunderbolt 2 after which once more to a most of 40 Gbps in 205 with Thunderbolt 3.
First-generation Thunderbolt and Thunderbolt 2 relied on a plug/jack model similar to Mini DisplayPort. This was conveniently what Apple had already adopted just a few years earlier than for exterior video connections, making the transition simpler—a minimum of inside that buyer phase.
With Thunderbolt 3, Intel adopted the USB-C type think about a very commonplace style. Thunderbolt 3 introduced a number of options and choices to the communication commonplace. That is what you must anticipate from any Thunderbolt 3 port on any pc or machine:
- 40 Gbps (jack solely): Thunderbolt 2 maxed out at 20 Gbps; all Thunderbolt 3 ports need to help 40 Gbps. Nevertheless, relying on the cable, you would possibly obtain solely 20 Gbps; see Thunderbolt Capabilities in Hyperlink Units with Cables.
- 4K shows: Every Thunderbolt 3 controller should help a minimum of a single 4K show at 60 Hz utilizing DisplayPort 1.2. Nevertheless, later variations of Thunderbolt 3 controllers might optionally incorporate DisplayPort 1.4 and deal with as much as two 4K shows at 60 Hz, one 4K show at 120 Hz, or one 5K show at 60 Hz. (The 5K possibility initially required a controller distinctive to Apple’s computer systems.)
- Minimal 15 W energy: The place Thunderbolt and Thunderbolt 2 needed to ship as much as 10 W, Thunderbolt 3 begins at 15 W, extra applicable for charging a later era of smartphones and tablets.
- Peer-to-peer networks: Thunderbolt permits computer systems to daisy chain collectively and obtain as much as 10 Gbps, as in the event that they had been related by 10 Gbps Ethernet. (See Use Peer-to-Peer 10 Gbps Thunderbolt.)
- Elective USB Energy Supply: With help for USB Energy Supply, a Thunderbolt 3 port can optionally push as much as 100 W of energy to a suitable machine, like a laptop computer.
- Elective hubs: Thunderbolt 3 might enable for as much as four-port Thunderbolt hubs. This function wasn’t typically supported till Thunderbolt 4 grew to become out there.
Thunderbolt 4 amps issues up a bit by rising minimal necessities or making optionally available Thunderbolt 3 options necessary in Thunderbolt 4.
The 2 largest modifications that may have an effect on you instantly are cable and compatibility enhancements. First, Thunderbolt 4 cables as much as 6.6 toes (2 m) don’t have the “energetic” circuitry requirement that was wanted in Thunderbolt 3 to attain 40 Gbps no matter cable size. Second, Thunderbolt 4 jacks should be totally backwards compatibility a minimum of 10 Gbps USB 3.1/3.2, however can help as much as 40 Gbps USB4.
The result’s the elimination of the foremost host/cable/peripheral compatibility that has dogged Thunderbolt. With a Thunderbolt 4 jack and Thunderbolt 4 cable:
- Any cable connecting a Thunderbolt 4 jack to a USB 3/USB4 peripheral port over USB-C will all the time work and all the time provide a minimum of a ten Gbps information fee.
- Primarily based on market analysis to this point, any Thunderbolt 4 cable can also be totally USB4 suitable. When connecting any two Thunderbolt 4, USB 3.x, or USB4 jacks with such a cable, you’ll all the time obtain the utmost frequent information fee.
This transformation alone ought to carry numerous reduction from cable litter, requirements confusion, and frustration over low information charges or incompatibility. However there’s extra! Right here’s what else you possibly can anticipate from Thunderbolt 4:
- All the time 40 Gbps: Thunderbolt 4 accepts no compromises. All jacks and cables should help 40 Gbps.
- Two 4K shows: Thunderbolt 3 might optionally deal with as much as two exterior 4K shows at 60 Hz; that’s now the minimal requirement for Thunderbolt 4.
- Required 100 W energy on a bunch: Any pc with Thunderbolt 4 will need to have a minimum of one jack that delivers as much as 100 W.
- Minimal USB help: As famous above, all Thunderbolt 4 jacks should help USB 3.2 Gen 2×1 and 1×2 (10 Gbps), however can optionally help as much as USB4 (20 Gbps and 40 Gbps).
- Wake from sleep: Whereas not a marquee function, Thunderbolt 4 requires {that a} host pc monitor the port for a “wake from sleep” sign. This enables a peripheral to wake the host. An identical function was added to Ethernet in 1996, referred to as Wake-from-LAN.
- Thunderbolt ports on dock: As a substitute of being an possibility, working methods and jacks should enable as much as 4 exterior Thunderbolt 4 ports on a dock.
USB and Thunderbolt compatibility
The most important space of port and cable confusion I ever encounter is the matrix of compatibility between generations of USB and Thunderbolt. It’s pure to be confused: the 2 have converged, however in what methods?
Listed below are the only methods to tell apart the capabilities of USB4 and Thunderbolt 4:
- Thunderbolt 4 is nearly completely a superset of USB4: Thunderbolt 4 has help for USB Energy Supply specification solely as much as 100 W. Some Thunderbolt 4 controllers won’t help 20 Gbps and 40 Gbps USB4, making it inconceivable for a USB4-based peripheral or host to exceed 10 Gbps between two gadgets.
- USB4 is a superset of Thunderbolt 3, not together with the necessary parts of Thunderbolt 4: USB4 requires a minimal of solely 20 Gbps, not 40 Gbps, making a USB4 controller on a bunch or peripheral probably slower than a pair of Thunderbolt 4 gadgets. It will possibly ship as much as 240 W of energy.
These variations largely apply when you’re have a high-performance atmosphere during which the distinction amongst 10, 20, and 40 Gbps throughput is essential. For most individuals, proudly owning a pc with a Thunderbolt 4 port and buying a ten Gbps USB 3.x or USB4 machine gained’t have a excessive affect.
But it surely additionally makes your selection of cables and peripherals shifting ahead far easier than previously.
First, when shopping for new peripherals test the capabilities of your pc or cellular machine. If it solely helps USB 3.0, 3.1, or 3.2, you possibly can go for what is often a far cheaper USB 3-only peripherals, like an SSD, than a Thunderbolt 3 or 4 mannequin. For Mac customers, you possibly can usually choose between USB 3.x and Thunderbolt 3 or 4 on the idea of efficiency and price as a result of Apple presents Thunderbolt 3 and USB 3.1 all from all new Macs beginning in 2016.
Second, when shopping for a brand new cable, your best option is nearly all the time a Thunderbolt 4/USB4 cable. Whereas Thunderbolt 3 cables had been fairly costly relative to USB-only ones, a brand new era of Thunderbolt 4/USB4 cables from many producers value about $25 to $60 from about half a foot to 2 meters. These cables are universally suitable amongst USB 3.1 and later and Thunderbolt 3 and later, and work with adapters with older requirements.
Third, keep away from two sorts of cables: “Charging-only” USB-C cables, which provide as much as 100 W of energy however solely 480 Mbps of knowledge; Apple nonetheless ships considered one of these with a few of its laptop computer fashions; and “energetic” Thunderbolt 3 cables when you work with a mixture of USB 3.x and Thunderbolt {hardware}. An energetic Thunderbolt 3 cable throttles USB to 480 Mbps as properly; a Thunderbolt 4/USB4 cable works on the full 5 Gbps to 40 Gbps fee out there throughout USB 3.0 to USB4.
Many of the compatibility confusions, cable litter, and port mismatches of the previous have disappeared with new requirements and cables. Preserve your self knowledgeable to get the very best outcomes with legacy gear, however you possibly can look ahead to a easy future.
This was an an edited excerpt from Glenn Fleishman’s new ebook, “Take Management of Untangling Connections,” a information to USB, Thunderbolt, DisplayPort, HDMI, Ethernet, and video connections and troubleshooting, out there from Take Management Books.

0 Comments